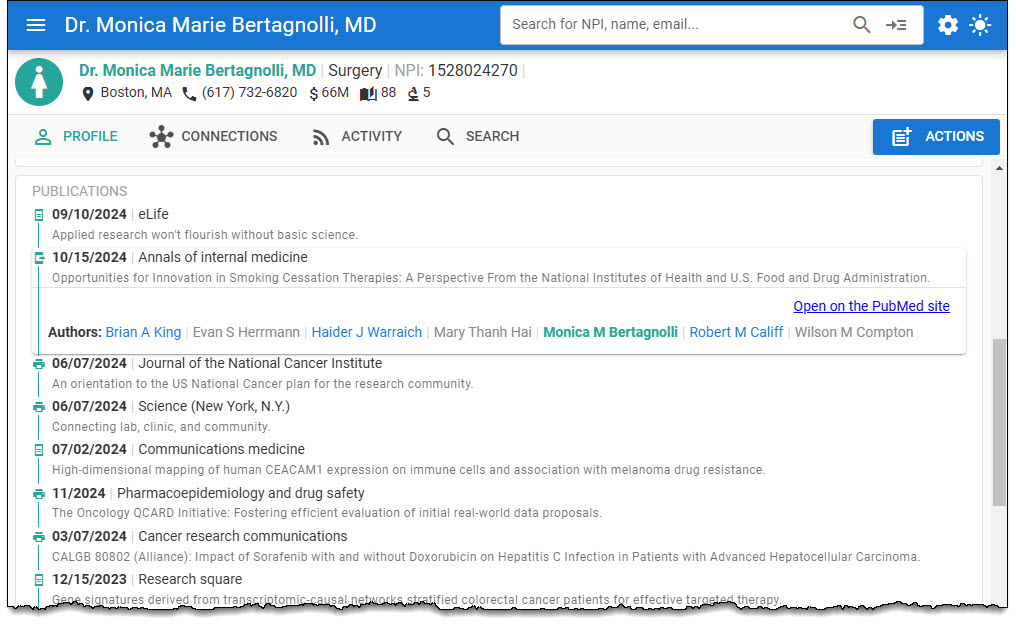
Explore publications for Healthcare Providers, Clinical Trial Investigators, and Key Opinion Leaders.
HealthProviders DB imports and matches the National Library of Medicine (NLM) PubMed publication citations with the Healthcare Provider’s Profile.
PubMed is a free resource for searching and retrieving biomedical and life sciences literature to improve health globally and personally.
You can open the PubMed citation from the Health Provider Profile.
In addition, you can click on other co-authors for the publication to view their profiles.
About the NLM PubMed Database
The PubMed database contains over 37 million citations and abstracts of biomedical literature, life science journals, and online books. It does not include full-text journal articles; however, links to the full text are often present when available from other sources, such as the publisher’s website or PubMed Central (PMC).
PubMed has been available to the public online since 1996. It was developed and maintained by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) at the U.S. National Library of Medicine (NLM), located at the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
Citations in PubMed primarily stem from the biomedicine and health fields and related disciplines such as life sciences, behavioral sciences, chemical sciences, and bioengineering.
PubMed facilitates searching across several NLM literature resources:
MEDLINE
MEDLINE is the most significant component of PubMed and consists primarily of citations from journals selected for MEDLINE; articles indexed with MeSH (Medical Subject Headings) and curated with funding, genetic, chemical, and other metadata.
PubMed Central (PMC)
Citations for PubMed Central (PMC) articles make up PubMed’s second most significant component.
PMC is a full-text archive that includes articles from journals reviewed and selected by NLM for archiving (current and historical) and individual articles collected for archiving in compliance with funder policies.
Bookshelf
The final component of PubMed is citations for books and some individual chapters available on Bookshelf.
Bookshelf is a full-text archive of books, reports, databases, and other biomedical, health, and life sciences documents.
The PubMed Data Collected
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Fore Name | Author’s first name. |
| Last Name | Author’s last name. |
| Initials | Author’s middle initial. |
| ORCID | Author’s ORCID. |
| Title | Journal title. |
| ArticleTitle | Article title in the journal. |
| Article ID | Article citation reference ID and type: doi pii pmcpid pmpid pmc mid sici pubmed medline pmcid |
| ISSN | Journal ISSN number. |
| PMID | PubMed article ID. |
| PubDate | Date the journal was published. |
| PubTypes | Mesh publication types. (e.g., Review, Letter, Retracted Publication, Clinical Conference, Research Support, N.I.H., Extramural) |
| Pub Model | Article publication medium/media: Print | Print-Electronic | Electronic | Electronic-Print | Electronic-eCollection |
| Publication Status | Article publication status: ppublish, epublcih, or ahead of print |
| Date Completed | Article end processing date. |
| Authors | Article authors. Authors are hyperlinked in Health Provides DB. |
| Keywords | Article keywords. You can search on keywords in Health Providers DB. |
| Chemicals | Article chemicals. You can search for chemicals in Health Providers DB. |

