HealthProviders DB is a comprehensive database of healthcare providers, including a complete directory of all Managed Care Organizations.
Managed Care Organizations (MCOs) are health plans that manage healthcare services to control costs while maintaining quality care through networks of contracted providers.
MCOs, such as HMOs and PPOs, employ strategies like preventive care, utilization management, and financial incentives to influence how members access services, thereby providing cost-effective, high-quality care.
Many states use MCOs to administer Medicaid and Medicare Advantage plans, receiving fixed payments per member to coordinate and deliver services.
MCOs in Public Health Programs
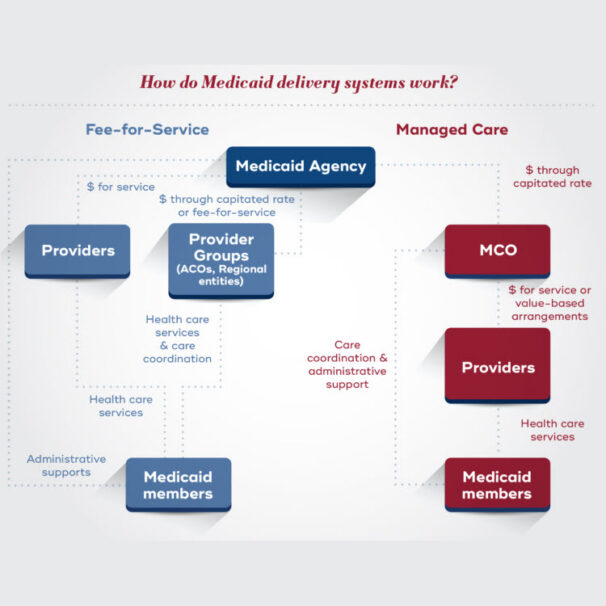
Medicaid
Many states contract with MCOs to manage their Medicaid programs, which provide health coverage for low-income individuals and families.
Medicare Advantage (Medicare Part C)
MCOs also offer Medicare benefits through Medicare Advantage plans, which are an alternative to the traditional Medicare program.
How MCOs Work
Contracting with Providers
MCOs enter into agreements with hospitals, doctors, specialists, and other healthcare facilities to offer services to their members at negotiated rates.
Network-Based Care
Members are encouraged or required to receive care within the MCO’s network of contracted providers, which helps control costs and ensure quality care.
Managed Care Principles
MCOs employ various strategies to manage healthcare delivery:
Preventive Medicine
Encouraging health and wellness to reduce the need for more expensive treatments.
Utilization Management
Reviewing and approving medical services to ensure they are medically necessary and delivered efficiently.
Financial Incentives
Using models like “capitation” (a fixed payment per member per month) to encourage MCOs and providers to manage resources effectively.
Treatment Guidelines
Developing and implementing standardized guidelines for medical care to ensure consistent, cost-effective treatment.
Health Maintenance Organizations (HMO)
Healthcare Taxonomy Code 302R00000X
A common type of MCO that provides comprehensive services through a network of providers and often requires a referral from a primary care physician (PCP) to see a specialist.
Members prepay a premium for the HMO’s health services, which generally include inpatient and ambulatory care.
Preferred Provider Organizations (PPO)
Healthcare Taxonomy Code 305R00000X
Another popular MCO model that offers more flexibility by allowing members to see both in-network and out-of-network providers, though at different cost levels.
A group of physicians and/or hospitals that contract with an employer to provide services to their employees is also a form of a PPO.
Exclusive Provider Organizations
Healthcare Taxonomy Code 302F00000X
An EPO is a form of PPO in which patients must visit a caregiver specified on its panel of providers (a participating provider).
Point of Services (POS)
Healthcare Taxonomy Code 305S00000X
These plans combine aspects of both HMOs and PPOs, offering greater provider choice but often requiring members to stay within the network to avoid higher costs.
This product may also be referred to as an open-ended HMO and offers a transition product that incorporates features of both HMOs and PPOs. Beneficiaries are enrolled in an HMO but can go outside the network for an additional cost.