HealthProviders DB is a comprehensive database of healthcare providers, including a complete directory of all Clinical Electrophysiology Physical Therapists.
Physical Therapist Healthcare Taxonomy Code 2251E1300X
As of today, the following are the total number of Clinical Electrophysiology Physical Therapists nationally, in your State, and near your location.
Select a State below to view the list by State. Additionally, you can narrow the list by city, among other options, from the Filter Panel, which you can open by clicking the vertical ellipses ⋮ in the upper right corner of the app.
Alaska – Alabama – Armed Forces Pacific – Arkansas – American Samoa – Arizona – California – Colorado – Connecticut – District of Columbia – Delaware – Florida – Federated States of Micronesia – Georgia – Guam – Hawaii – Iowa – Idaho – Illinois – Indiana – Kansas – Kentucky – Louisiana – Massachusetts – Maryland – Maine – Marshall Islands – Michigan – Minnesota – Missouri – Northern Mariana Islands – Mississippi – Montana – North Carolina – North Dakota – Nebraska – New Hampshire – New Jersey – New Mexico – Nevada – New York – Ohio – Oklahoma – Oregon – Pennsylvania – Puerto Rico – Palau – Rhode Island – South Carolina – South Dakota – Tennessee – Texas – Utah – Virginia – Virgin Islands – Vermont – Washington – Wisconsin – West Virginia – Wyoming
Medicare
The following are the total number of Clinical Electrophysiology Physical Therapists who accept Medicare in your State, the number who have opted out of Medicare, and the total number excluded from participation in Medicare nationwide.
The diagram below shows all the Clinical Electrophysiology Physical Therapists across the country, represented by blue bubbles. The larger the bubble, the greater the concentration of providers in that area. Red bubbles represent Medicare-excluded providers, with the larger bubbles indicating a higher percentage of excluded providers in that region. You can change the bubble size to be based on exclusions from the Size menu.
What do Clinical Electrophysiology Physical Therapists do?
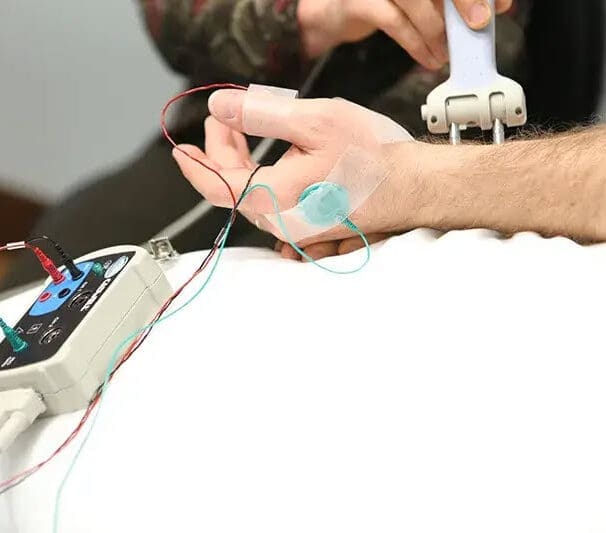
Clinical electrophysiology physical therapists utilize electrical currents to diagnose and treat neurological and musculoskeletal conditions. They perform tests such as nerve conduction studies (NCS) and electromyography (EMG) to assess nerve and muscle function, and employ electrotherapy for healing, pain relief, and tissue repair.
They interpret the resulting electrophysiologic data to identify the extent and cause of a patient’s dysfunction and to develop appropriate management plans.
Diagnose conditions: They conduct NCS and EMG tests, which use electrodes to measure electrical activity in muscles and nerves.
Interpret test results: They analyze test data to identify the location and severity of muscle or nerve problems, such as neuropathies or myopathies.
Treat conditions: They use electrotherapy to:
- Reduce pain and muscle spasms.
- Promote blood circulation.
- Aid in wound healing for various types of injuries and ulcers.
- Improve joint mobility and tissue repair.
Develop treatment plans: Based on diagnostic findings, they propose recommendations and interventions to support patients’ recovery.
Common conditions they treat
- Various wounds, including diabetic ulcers and post-surgical incisions
- Entrapment neuropathies (e.g., carpal tunnel syndrome)
- Radiculopathy
- Peripheral neuropathies
- Myopathies (muscle diseases)
- Neuromuscular junction defects
- Chronic pain